9.5 Theories and measurements of Intelligence
Intelligence is among the oldest and longest studied topics in all of psychology. The development of assessments to measure this concept is at the core of the development of psychological science itself. This chapter introduces key historical figures, major theories of intelligence, and common assessment strategies related to intelligence. This chapter will also discuss controversies related to the study of group differences in intelligence.

Every year hundreds of grade school students converge on Washington, D.C., for the annual Scripps National Spelling Bee. The “bee” is an elite event in which children as young as 8 square off to spell words like “cymotrichous” and “appoggiatura.” Most people who watch the bee think of these kids as being “smart” and you likely agree with this description.
What makes a person intelligent? Is it heredity (two of the 2014 contestants in the bee have siblings who have previously won; National Spelling Bee, 2014a)? Is it interest (the most frequently listed favorite subject among spelling bee competitors is math; NSB, 2014b)? In this chapter we will cover these and other fascinating aspects of intelligence; we will attempt to define it, discuss approaches to measure it, and address some of the complications involved in interpreting and applying the results.
Defining and Measuring Intelligence
When you think of “smart people” you likely have an intuitive sense of the qualities that make them intelligent. Maybe you think they have a good memory, or that they can think quickly, or that they simply know a whole lot of information. Indeed, people who exhibit such qualities appear very intelligent. That said, it seems that intelligence must be more than simply knowing facts and being able to remember them. One point in favor of this argument is the idea of animal intelligence. It will come as no surprise to you that a dog, which can learn commands and tricks seems smarter than a snake that cannot. In fact, researchers and lay people generally agree with one another that primates—monkeys and apes (including humans)—are among the most intelligent animals. Apes such as chimpanzees are capable of complex problem solving and sophisticated communication (Kohler, 1924).
Scientists point to the social nature of primates as one evolutionary source of their intelligence. Primates live together in troops or family groups and are, therefore, highly social creatures. As such, primates tend to have brains that are better developed for communication and long term thinking than most other animals. For instance, the complex social environment has led primates to develop deception, altruism, numerical concepts, and “theory of mind” (a sense of the self as a unique individual separate from others in the group; Gallup, 1982; Hauser, MacNeilage & Ware, 1996).
The question of what constitutes human intelligence is one of the oldest inquiries in psychology. When we talk about intelligence we typically mean intellectual ability. This broadly encompasses the ability to learn, remember and use new information, to solve problems and to adapt to novel situations. An early scholar of intelligence, Charles Spearman, proposed the idea that intelligence was one thing, a “general factor” sometimes known as simply “g.” He based this conclusion on the observation that people who perform well in one intellectual area such as verbal ability also tend to perform well in other areas such as logic and reasoning (Spearman, 1904).
A contemporary of Spearman’s named Francis Galton—himself a cousin of Charles Darwin– was among those who pioneered psychological measurement (Hunt, 2009). For three pence Galton would measure various physical characteristics such as grip strength but also some psychological attributes such as the ability to judge distance or discriminate between colors. This is an example of one of the earliest systematic measures of individual ability. Galton was particularly interested in intelligence, which he thought was heritable in much the same way that height and eye color are. He conceived of several rudimentary methods for assessing whether his hypothesis was true. For example, he carefully tracked the family tree of the top-scoring Cambridge students over the previous 40 years. Although he found specific families disproportionately produced top scholars, intellectual achievement could still be the product of economic status, family culture or other non-genetic factors. Galton was also, possibly, the first to popularize the idea that the heritability of psychological traits could be studied by looking at identical and fraternal twins. Although his methods were crude by modern standards, Galton established intelligence as a variable that could be measured (Hunt, 2009).
Development of the Stanford-Binet Test

The person best known for formally pioneering the measurement of intellectual ability is Alfred Binet. Like Galton, Binet was fascinated by individual differences in intelligence. For instance, he blindfolded chess players and saw that some of them had the ability to continue playing using only their memory to keep the many positions of the pieces in mind (Binet, 1894). Binet was particularly interested in the development of intelligence, a fascination that led him to observe children carefully in the classroom setting.
Along with his colleague Theodore Simon, Binet created a test of children’s intellectual capacity. They created individual test items that should be answerable by children of given ages. For instance, a child who is three should be able to point to her mouth and eyes, a child who is nine should be able to name the months of the year in order, and a twelve year old ought to be able to name sixty words in three minutes. Their assessment became the first “IQ test.”

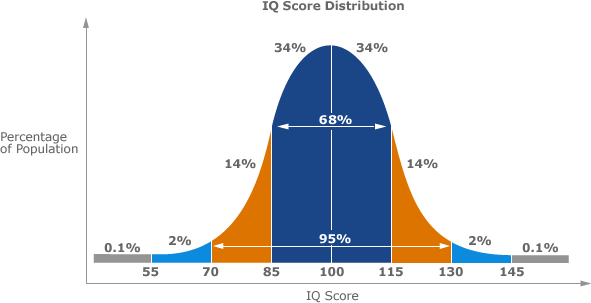
“IQ” or “intelligence quotient” is a name given to the score of the Binet-Simon test. The score is derived by dividing a child’s mental age (the score from the test) by their chronological age to create an overall quotient. These days, the phrase “IQ” does not apply specifically to the Binet-Simon test and is used to generally denote intelligence or a score on any intelligence test. In the early 1900s the Binet-Simon test was adapted by a Stanford professor named Lewis Terman to create what is, perhaps, the most famous intelligence test in the world, the Stanford-Binet (Terman, 1916). The major advantage of this new test was that it was standardized. Based on a large sample of children Terman was able to plot the scores in a normal distribution, shaped like a “bell curve” (see Fig. 1). To understand a normal distribution think about the height of people. Most people are average in height with relatively fewer being tall or short, and fewer still being extremely tall or extremely short. Terman (1916) laid out intelligence scores in exactly the same way, allowing for easy and reliable categorizations and comparisons between individuals.
Looking at another modern intelligence test—the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)—can provide clues to a definition of intelligence itself. Motivated by several criticisms of the Stanford-Binet test, psychologist David Wechsler sought to create a superior measure of intelligence. He was critical of the way that the Stanford-Binet relied so heavily on verbal ability and was also suspicious of using a single score to capture all of intelligence. To address these issues Wechsler created a test that tapped a wide range of intellectual abilities. This understanding of intelligence—that it is made up of a pool of specific abilities—is a notable departure from Spearman’s concept of general intelligence. The WAIS assesses people’s ability to remember, compute, understand language, reason well, and process information quickly (Wechsler, 1955).
One interesting by-product of measuring intelligence for so many years is that we can chart changes over time. It might seem strange to you that intelligence can change over the decades but that appears to have happened over the last 80 years we have been measuring this topic. Here’s how we know: IQ tests have an average score of 100. When new waves of people are asked to take older tests they tend to outperform the original sample from years ago on which the test was normed. This gain is known as the Flynn Effect, named after James Flynn, the researcher who first identified it (Flynn, 1987). Several hypotheses have been put forth to explain the Flynn Effect including better nutrition (healthier brains!), greater familiarity with testing in general, and more exposure to visual stimuli. Today, there is no perfect agreement among psychological researchers with regards to the causes of increases in average scores on intelligence tests. Perhaps if you choose a career in psychology you will be the one to discover the answer!
Types of Intelligence
David Wechsler’s approach to testing intellectual ability was based on the fundamental idea that there are, in essence, many aspects to intelligence. Other scholars have echoed this idea by going so far as to suggest that there are actually different types of intelligence. Take the concepts of “street smarts” and “book learning” for example. The former refers to practical wisdom accumulated through experience while the latter indicates formal education. A person high in street smarts might have a superior ability to catch a person in a lie, to persuade others, or to think quickly under pressure. A person high in book learning, by contrast, might have a large vocabulary and be able to remember a large number of references to classic novels. Although psychologists don’t use street smarts or book smarts as professional terms they do believe that intelligence comes in different types.
There are many ways to parse apart the concept of intelligence. Many scholars believe that Carroll‘s (1993) review of more than 400 data sets provides the best currently existing single source for organizing various concepts related to intelligence. Carroll divided intelligence into three levels, or strata, descending from the most abstract down to the most specific (see Fig. 2). In the same manner, Carroll called the highest level (stratum III) the general intelligence factor “g.” Under this were more specific stratum II categories such as fluid intelligence and visual perception and processing speed. Each of these, in turn, can be sub-divided into very specific components such as spatial scanning, reaction time, and word fluency.
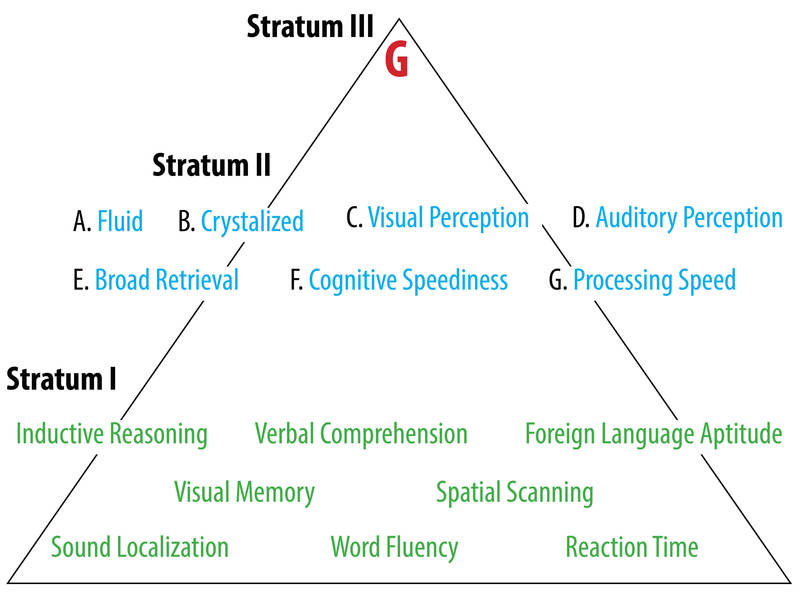
Thinking of intelligence as Carroll (1993) does, as a collection of specific mental abilities, has helped researchers conceptualize this topic in new ways. For example, Horn and Cattell (1966) distinguish between “fluid” and “crystalized” intelligence, both of which show up on stratum II of Carroll’s model. Fluid intelligence is the ability to “think on your feet;” that is, to solve problems. Crystalized intelligence, on the other hand, is the ability to use language, skills and experience to address problems. The former is associated more with youth while the latter increases with age. You may have noticed the way in which younger people can adapt to new situations and use trial and error to quickly figure out solutions. By contrast, older people tend to rely on their relatively superior store of knowledge to solve problems.
Harvard professor Howard Gardner is another figure in psychology who is well-known for championing the notion that there are different types of intelligence. Gardner’s theory is appropriately, called “multiple intelligences.” Gardner’s theory is based on the idea that people process information through different “channels” and these are relatively independent of one another. He has identified 8 common intelligences including 1) logic-math, 2) visual-spatial, 3) music-rhythm, 4) verbal-linguistic, 5) bodily-kinesthetic, 6) interpersonal, 7) intrapersonal, and 8) naturalistic (Gardner, 1985). Many people are attracted to Gardner’s theory because it suggests that people each learn in unique ways. There are now many Gardner- influenced schools in the world.
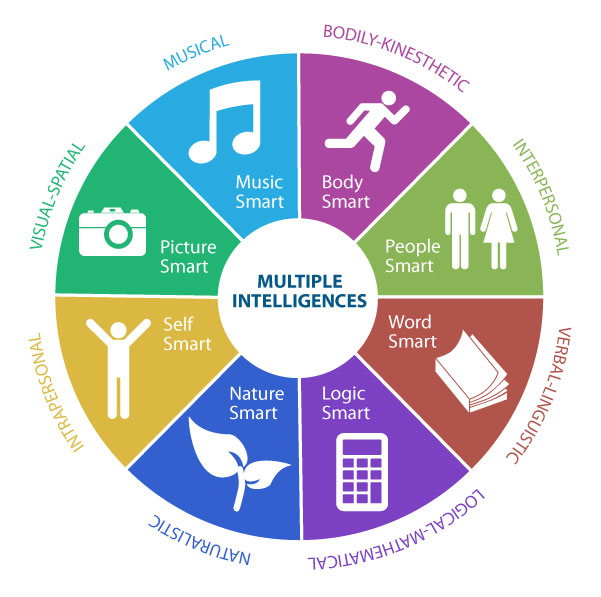
However, it’s worth noting that many psychologists have criticized Gardner’s theory due to a lack of evidence that the proposed types of “intelligence” are independent from each other (Waterhouse, 2023); in fact, several of these factors tend to correlate with Spearman’s G. Part of this complication then stems from the difficulty of defining intelligence, especially as something that can be defined independently of results on an “intelligence” measure. We will return to this complication in a later section.
Another type of intelligence is Emotional intelligence. Unlike traditional models of intelligence that emphasize cognition (thinking) the idea of emotional intelligence emphasizes the experience and expression of emotion. Some researchers argue that emotional intelligence is a set of skills in which an individual can accurately understand the emotions of others, can identify and label their own emotions, and can use emotions. (Mayer & Salovey, 1997). Other researchers believe that emotional intelligence is a mixture of abilities, such as stress management, and personality, such as a person’s predisposition for certain moods (Bar-On, 2006). Regardless of the specific definition of emotional intelligence, studies have shown a link between this concept and job performance (Lopes, Grewal, Kadis, Gall, & Salovey, 2006).
There is one last point that is important to bear in mind about intelligence. It turns out that the way an individual thinks about his or her own intelligence is also important because it predicts performance. Researcher Carol Dweck has made a career out of looking at the differences between high IQ children who perform well and those who do not, so-called “under achievers.” Among her most interesting findings is that it is not gender or social class that sets apart the high and low performers. Instead, it is their mindset. The children who believe that their abilities in general (and their intelligence specifically) are fixed traits tend to underperform. By contrast, kids who believe that intelligence is changeable and evolving tend to handle failure better and perform better (Dweck, 1986). Dweck refers to this as a person’s “mindset” and having a growth mindset appears to be healthier.
The ability to derive information, learn from experience, adapt to the environment, understand, and correctly utilize thought and reason.
A cognitive-ability and intelligence test that has been used to diagnose developmental or intellectual deficiencies in young children.
The gradual cross-cultural rise in raw scores obtained on measures of general intelligence. These increases have been roughly 9 points per generation (i.e., 30 years). The gains have been unequally distributed across the different kinds of abilities, with fluid abilities showing substantially greater gains than crystallized abilities.
The proposed set of mental processes that is used in dealing with relatively novel tasks.
The sum of one’s knowledge including vocabulary and general information.

